- Thread is a flow of execution
- Thread is light weight process
- Thread is applyed on programang level only
Tuesday, 18 February 2020
What is thread?
Friday, 14 December 2018
what is c programming
C is a programming language developed at AT & T’s Bell Laboratories of USA in 1972. It was designed and written by a man named Dennis Ritchie. In the late seventies C began to replace the more familiar languages of that time like PL/I, ALGOL, etc. No one pushed C. It wasn’t made the ‘official’ Bell Labs language. Thus, without any advertisement C’s reputation spread and its pool of users grew. Ritchie seems
what is c programming language
c programming language is not a high level language and it is not a low level language, it is medium level language
Sunday, 6 September 2015
Data types in C
There are different data types those are:
1 Integer
2 Character
3 Float
the above three data types are more important to use in c programming
Integer:
we use size of the integer is 2 Byte and %d is data type in c standard function. the range of the integer is -32768 to 32767.
1 Integer
2 Character
3 Float
the above three data types are more important to use in c programming
Integer:
we use size of the integer is 2 Byte and %d is data type in c standard function. the range of the integer is -32768 to 32767.
- An integer constant must have at least one digit.
- It must not have a decimal point.
- It can be either positive or negative.
- If no sign precedes an integer constant it is assumed to be
- positive.
- No commas or blanks are allowed within an integer constant.
- The allowable range for integer constants is -32768 to 32767.
Character:
Size of the character is 1 Bytes and %c is data types use in c standard function.
A character constant is a single alphabet, a single digit or a single special symbol enclosed within single inverted commas. Both the inverted commas should point to the left. For example, ’A’ is a valid character constant whereas ‘A’ is not.
The maximum length of a character constant can be 1 character.
Ex.: 'A'
'I'
'5'
'='
Float:
Real constants are often called Floating Point constants. The real constants could be written in two forms—Fractional form and Exponential form. Following rules must be observed while constructing real constants expressed in fractional form:
- A real constant must have at least one digit.
- It must have a decimal point.
- It could be either positive or negative.
- Default sign is positive.
- No commas or blanks are allowed within a real constant.
Ex.: +325.34
426.0
-32.76
-48.5792
Introduction on C Programming
What is C?
C is a programming language developed at AT & T’s Bell Laboratories of USA in 1972. It was designed and written by a man named Dennis Ritchie. In the late seventies C began to replace the more familiar languages of that time like PL/I, ALGOL, etc. No one pushed C. It wasn’t made the ‘official’ Bell Labs language. Thus, without any advertisement C’s reputation spread and its pool of users grew. Ritchie seems to have been rather surprised that so many programmers preferred C to older languages like FORTRAN or PL/I, or the newer ones like Pascal and APL. But, that's what happened. Possibly why C seems so popular is because it is reliable, simple and easy to use. Moreover, in an industry where newer languages, tools and technologies emerge and vanish day in and day out, a language that has survived for more than 3 decades has to be really good.
C is a programming language developed at AT & T’s Bell Laboratories of USA in 1972. It was designed and written by a man named Dennis Ritchie. In the late seventies C began to replace the more familiar languages of that time like PL/I, ALGOL, etc. No one pushed C. It wasn’t made the ‘official’ Bell Labs language. Thus, without any advertisement C’s reputation spread and its pool of users grew. Ritchie seems to have been rather surprised that so many programmers preferred C to older languages like FORTRAN or PL/I, or the newer ones like Pascal and APL. But, that's what happened. Possibly why C seems so popular is because it is reliable, simple and easy to use. Moreover, in an industry where newer languages, tools and technologies emerge and vanish day in and day out, a language that has survived for more than 3 decades has to be really good.
Wednesday, 9 July 2014
Different types of Routing methods
Different types of Routing methods:
there are four type of routing methods are there those are:
1 Fixed
2 Flooding
3 Random
4 Adaptive
2 Flooding
3 Random
4 Adaptive
1 Fixed Routing:
1 Single permanent route for each source to destination pair
2 Determine routes using a least cost algorithm
3 Route fixed, at least until a change in network topology
2) Flooding:
1 No network info required Packet sent by node to every neighbor
2 Incoming packets re transmitted on every link except
incoming link
3 Eventually a number of copies will arrive at destination
4 Each packet is uniquely numbered so duplicates can be
discarded
5 Nodes can remember packets already forwarded to keep
network load in bounds
6 Can include a hop count in packets
3 Random:
1 Node selects one outgoing path for re transmission of
incoming packet
2 Selection can be random or round robin
3 Can select outgoing path based on probability calculation
4 No network info needed
5 Route is typically not least cost nor minimum hop
4 Adaptive:
1 Used by almost all packet switching networks
2 Routing decisions change as conditions on the network
change
1Failure
2 Congestion
3 Requires info about network
4 Decisions more complex
5 Tradeoff between quality of network info and overhead
6 Reacting too quickly can cause oscillation
7 Too slowly to be relevant
Tuesday, 8 July 2014
Segmentation vs. Fragmentationa
Segmentation
vs. Fragmentation:
Segmentation
is basically the same as fragmentation, with a few differences:
Fragmentation (IP layer):
only occurs when transmitting a
packet whose size is larger than the MTU of the estination network
Any router (connecting two
different network types) could theoretically fragment ackets
Fragmentation can almost be
considered an emergency practice (what to do when omething goes wrong)
Segmentation (TCP layer):
Occurs for all data streams, to
divide the data into packets (above TCP layer data is ontinuous)
Only the source host will segment
packets
Segmentation is a normal part of
TCP’s job
Shortest-Job-First (SJF) Scheduling with example
Shortest-Job-First (SJF) Scheduling:
- Associate with each process the length of its next CPU burst.Use these lengths to schedule the process with the shortest time
- Two schemes:
- l nonpreemptive – once CPU given to the process it cannot be preempted until completes its CPU burst
- l preemptive – if a new process arrives with CPU burst length less than remaining time of current executing process, preempt. This scheme is know as the Shortest-Remaining-Time-First (SRTF)
- SJF is optimal – gives minimum average waiting time for a given set of processes
First-Come, First-Served (FCFS) Scheduling with Example
First-come, first-served (FCFS): – sometimes first-in, first-served and first-come, first choice – is a service policy whereby the requests of customers or clients are attended to in the order that they arrived, without other biases or preferences. The policy can be employed when processing sales orders, in determining restaurant seating, on a taxi stand, etc. In Western society, it is the standard policy for the processing of most queues in which people wait for a service that was not prearranged or pre-planned.
Example 1:
Monday, 7 July 2014
Adaptive Routing and its advantages
Adaptive Routing:
- Adaptive Routing used by almost all packet switching networks
- Routing decisions change as conditions on the network change
- Failure
- Congestion
- Requires info about network
- Decisions more complex
- Trade off between quality of network info and overhead
- Reacting too quickly can cause oscillation
- Too slowly to be relevant
2) Aid congestion control
3) Complex system
4)May not realize theoretical benefits
What are the Properties of Flooding?
- All possible routes are tried
- Very robust
- At least one packet will have taken minimum hop count route
- Can be used to set up virtual circuit
- All nodes are visited
- Useful to distribute information (e.g. routing)
What is flooding?
- No network info required
- Packet sent by node to every neighbor
- Incoming packets re transmitted on every link except incoming link
- Eventually a number of copies will arrive at destination
- Each packet is uniquely numbered so duplicates can be discarded
- Nodes can remember packets already forwarded to keep network load in bounds
- Can include a hop count in packets
Sunday, 6 July 2014
what are the different type of networks
Different type of networks are :
- LAN
- MAN
- WAN
Local Area Network(LAN): LAN is only limited space cover like one bulling, college,university and industry.we can send data very efficient to delivery on node to other.
Local Area Network
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN): Metropolitan area network is it cover only city's and big industry.
metropolitan area network
Saturday, 28 June 2014
Difference in virtual packet switching and datagram switching
Virtual Circuit Packet Switching
1. Virtual circuits allow packets to contains circuit number instead of full destination address so less router memory and bandwidth require. Thus cost wise it is cheaper.
2. Virtual circuit requires a setup phase, which takes time and consume resources.
3. In virtual circuit, router just uses the circuit number to index into a table to find out where the packet goes.
4. Virtual circuit has some advantages in
avoiding congestion within the subnet
Because resources can be reserved in advance, when the connection is established.
5. Virtual circuit have some problem.
It a router crashes and loses its memory,
even it come back up a second later, all the
virtual circuits passing through it will have
to be aborted.
6. The loss fault on communication line
vanishes the virtual circuits.
7. In virtual circuit a fixed path is used during
transmission so traffic throughout the
subnet can not balanced. It cause congestion problem.
8. A virtual circuit is a implementation of connection oriented service.
Datagram Packet Switching
1. Datagram circuits allow packets to contains full address instead of circuit number so each packet has significant amount of overhead, and hence wasted band width. Thus it is costly.
2. Datagram circuit does not require setup phase , so no resources are consumed.
3. In datagram circuit, a more complicated procedure is required to determine where the packet goes.
4. In a datagram subnet, congestion avoidance is more difficult.
5. In datagram circuit if a router goes down only those user whose packets were queued up in the router at the time will suffer.
6. The loss or fault on communication line can be easily compensated in datagram circuits.
7. Datagram allow the router to balance the traffic throughout the subnet, since router can be changed halfway through a connection.
1. Virtual circuits allow packets to contains circuit number instead of full destination address so less router memory and bandwidth require. Thus cost wise it is cheaper.
2. Virtual circuit requires a setup phase, which takes time and consume resources.
3. In virtual circuit, router just uses the circuit number to index into a table to find out where the packet goes.
4. Virtual circuit has some advantages in
avoiding congestion within the subnet
Because resources can be reserved in advance, when the connection is established.
5. Virtual circuit have some problem.
It a router crashes and loses its memory,
even it come back up a second later, all the
virtual circuits passing through it will have
to be aborted.
6. The loss fault on communication line
vanishes the virtual circuits.
7. In virtual circuit a fixed path is used during
transmission so traffic throughout the
subnet can not balanced. It cause congestion problem.
8. A virtual circuit is a implementation of connection oriented service.
Datagram Packet Switching
1. Datagram circuits allow packets to contains full address instead of circuit number so each packet has significant amount of overhead, and hence wasted band width. Thus it is costly.
2. Datagram circuit does not require setup phase , so no resources are consumed.
3. In datagram circuit, a more complicated procedure is required to determine where the packet goes.
4. In a datagram subnet, congestion avoidance is more difficult.
5. In datagram circuit if a router goes down only those user whose packets were queued up in the router at the time will suffer.
6. The loss or fault on communication line can be easily compensated in datagram circuits.
7. Datagram allow the router to balance the traffic throughout the subnet, since router can be changed halfway through a connection.
CIDR Notation
•Inside
the computer each address mask is stored as a 32 bit value in binary, which is
then expressed in dotted octet notation.
•The
new CIDR notation append a slash and the size of the mask in decimal notation:
For example 128.10.0.0/16
CIDR
Address Block Example
•Suppose
an ISP has a single Class B license 128.211.00.0. Using a classful address scheme, he/she can only assign the
prefix to one customer, who can have up to 216 host
addresses.
•Using
CIDR, the ISP could assign the entire prefix to a single organization by using
128.211.0.0/16
•Or he
could partition the address into three pieces (two of them big enough for 2
customers with 12 computers each and the remainder available for future use.
••One customer could be assigned 128.211.0.16/28
•and the other could be assigned 128.211.0.32/28
•Both customers have the same mask size (28
bits), but the prefixes differ and each has a unique prefix. More importantly the ISP retains most of the
addresses, which can then be assigned to other customers.
•
Routers and Addresses
•Routers compare the network prefix portion of
the address to a value in their routing tables.
•Suppose a router is given a
destination address, D and a pair (A,M) that
represents the 32 bit address and
the 32 bit subnet mask.
•To make the comparison, the
router tests the logical "and" condition to set
the host bits of
address D to zero and then compares the result with the network prefix A:
A
== ( D & M)
•For
example consider this 32 bit mask:
(255.255.0.0
in decimal)
11111111 11111111 00000000
00000000
and the network prefix (128.10.0.0 in
decimal):
10000000 00001010 00000000
00000000
•Now
consider the 32 bit destination address
128.10.2.3 which has the binary
equivalent of
10000000 00001010 00000010
00000011
•The
logical "and" between the destination address and the address mask
produces the result:
10000000 00001010 00000000
00000000
•which
is equal to the prefix 128.10.0.0
•
Address Masks in Networks
• How can an IP address be divided at an
arbitrary boundary?
•It requires an additional piece of
information to be stored with each address. This information specifies the
exact boundary between the network prefix and the host suffix.
•To use classless or subnet addressing the
routers must store 2 pieces of information:
–the 32
bit address and
–another
32 bit value that specifies the boundary between the prefix and suffix.
•This second value is called the called the subnet mask
and 1 bits mark the network prefix and zero bits mark the host portion. This
makes computation efficient.
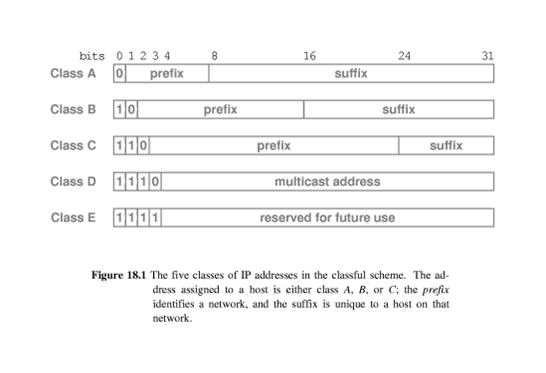
IP Addressing
IP Addressing
· Octet (8-bit)
boundaries are used to
partition an
address into prefix and suffix
· Class A,
B and C are primary classes
· Used for ordinary host
addressing
· Class D is used for multicast, a limited
form of
broadcast
· Internet hosts join a multicast
group
· Packets are delivered to
all members of
group
· Routers manage delivery of
single packet
from source to all members of multicast
group
· Used for MBone (multicast backbone)
· Class E is reserved ( for future use)
· IP software computes the class of the
destination address when it receives a packet.
· IP addresses are self-identifying because the
class can be computed directly from the first few bits of the address
· The first 4 (leading) bits of the address
denote the class:
–Class A begins with 0
–Class B begins with 10
–Class C begins with 110
difference between circuit-switched and packet-switched networks?
Packet
Switching:
ØIn packet-based networks, the message gets broken into small data
packets.
ØThese packets are sent out from the computer
and they travel around the network seeking out the most efficient route to
travel as circuits become available.
ØThis does not necessarily mean that they seek
out the shortest route.
ØEach packet may go a different route from the
others
Advantages:
- Security
- Bandwidth used to full potential
- Devices of different speeds can communicate
- Not affected by line failure (redirects signal)
- Availability – no waiting for a direct connection to become available
- During a crisis or disaster, when the public telephone network might stop working, e-mails and texts can still be sent via packet switching
Disadvantages
»Under heavy use there can be a delay
»Data packets can get lost or become corrupted
»Protocols are needed for a reliable transfer
»Not so good for some types data streams (e.g.
real-time video streams can lose frames due to the way packets arrive out of
sequence)
Circuit
Switching:
ØCircuit switching was designed in 1878 in order to send telephone
calls down a dedicated channel.
ØThis channel remains open and in use
throughout the whole call and cannot be used by any other data or phone calls.
Advantages
»Circuit is dedicated to the call
–
no interference, no sharing
»Guaranteed the full bandwidth
for
the duration of the call
»Guaranteed quality of service
Disadvantages
»Inefficient – the equipment may
be
unused for a lot of the call; if no data is
being sent, the dedicated line
still
remains open.
»It takes a relatively long time
to set up
the circuit.
»During a crisis or disaster, the
network
may become unstable or unavailable.
»It was primarily developed for
voice
traffic rather than data traffic.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)



.jpg)